Generators generate electricity. Although it’s a lot more complicated than that, that’s their main function.
However, there are AC and DC generators, and if you need a generator for whatever reason, then you’re likely wondering what the difference between the two types are.
Does it matter which generator you go with? The short answer is yes.
Some generators are better-suited for residential purposes, and others for commercial purposes.
To help you decide which generator you should choose, here are the differences between AC and DC generators.
The difference between AC and DC generators
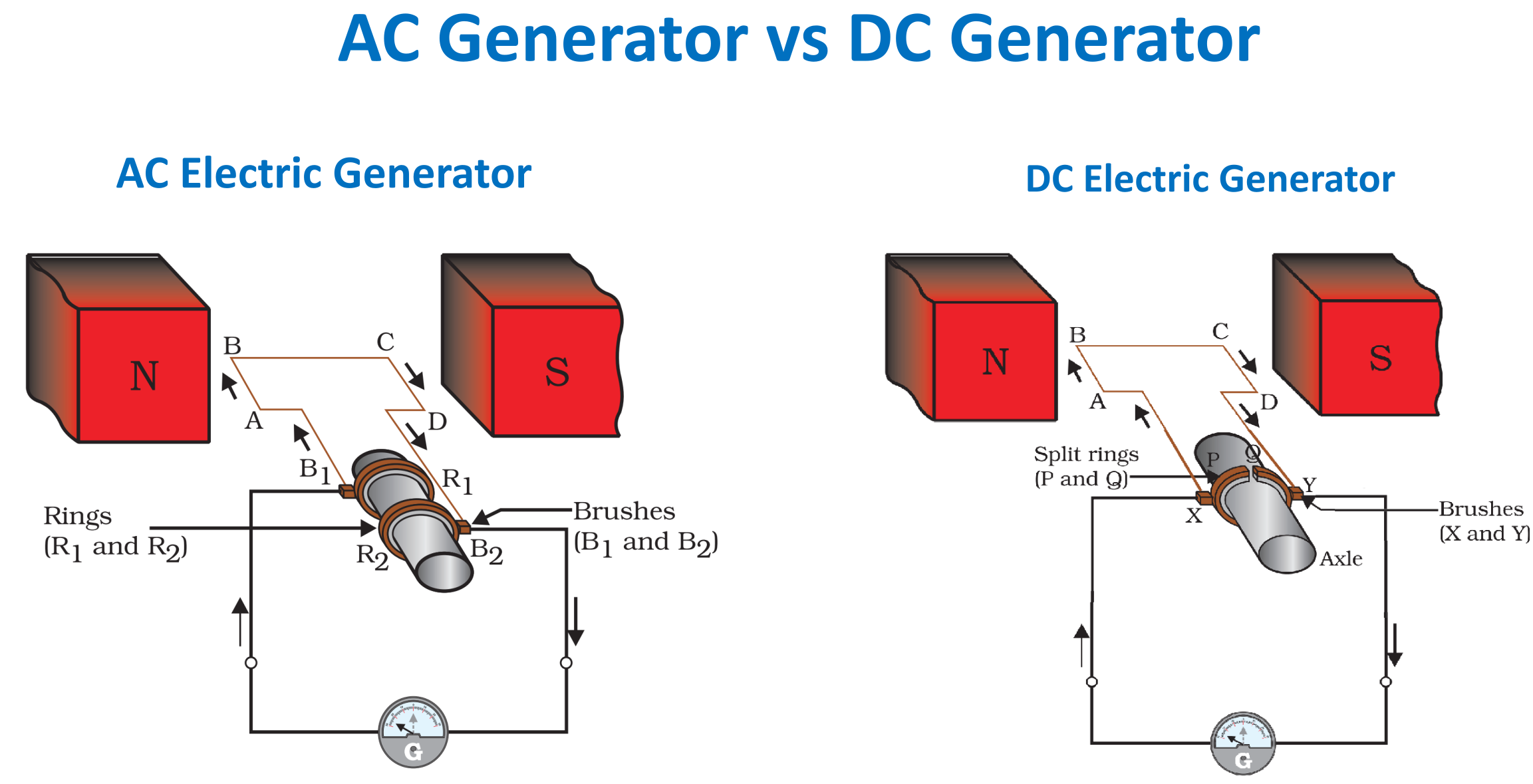
According to It Still Works, “In an AC, or alternating current, generator, the electrical current periodically reverses direction.”
With a DC, or direct current generator, the current flows in one direction; however, they both, of course, “produce currents via electromagnetic induction.”
In terms of primary uses, which is probably what you’re trying to compare between the two generators, these generators serve different purposes.
For example, homes typically have AC generators installed in them because they power common electrical appliances, such as vacuums, blenders, etc.
DC generators, on the other hand, power much larger electrical components and motors. As an example, DC generators are used to power the subway systems.
In most cases, if you need a new generator for residential purposes or your home, then you will want to purchase an AC generator. However, if you have large equipment (including motors), then you might consider a DC generator. That’s for an extreme case, though, because, once again, DC generators are powerful enough to power a subway system. They aren’t typically needed for everyday appliances in a home, such as a coffee machine.
There are other differences as well.
As BYJU’S learning app points out, differences also exist in the design, commutators, rings, short circuit possibility, armature, rotating parts, current induction, output voltage, maintenance, types, cost, distribution and transmission, efficiency, and applications.
While all of those differences are important and help to give you a better understanding of how each generator works in great detail, and we encourage you to follow the link above to see these differences mapped out, assuming you’re in the market for a generator.
What do you need to power? The answer to that question will help you identify, differences or not, what generator is best for you. It really depends on the type of business, how many things need power, whether large motors are being used or not, and similar questions.
As an example, if you work from home and don’t have large appliances, then an AC generator is more than adequate.
Whether you’re a large company and need to power large motors, or you’re in the market for an AC generator to power common electrical appliances, it’s a good idea to check out generators made by Welland Power.
These UK-made diesel generators are ideal for residential and commercial purposes alike. You can even purchase a custom diesel generator, which are made to project specifications. And, although these are made in the UK, Welland Power supplies them for industrial buildings and sites in Europe, the Middle East, South America/Caribbean, and Asia.
You’ll find many differences between AC and DC generators, although both types, in theory, do the same thing, which is generate electricity. However, AC generators tend to be used for residential purposes and DC generators for commercial purposes. AC generators power smaller electrical items, and DC generators power larger electric motors. The type of generator you need comes down to the size of your company and what you will need powered.
To read more on topics like this, check out the business tips category.